class AlexNet(nn.Module):
# ...
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x = self.features(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
[python 문법] 함수 선언시 "->"와 ":"의 의미 :
def func_name(param1 : int, param2 : str) -> int:
return 0위의 예시와 같이 "->"와 ":"가 붙는 경우, 위와 같은 표현들은 function annoation으로 주석의 역할을 한다. 코드 상의 기능을 하지 않고 보충 설명을 해주는 것으로, 여기서 지정한 것과 다른 형태를 사용하더라도 문제 없이 작동한다.
화살표("->")의 경우 해당 함수의 return 값의 형태에 대한 주석이다. 콜론(":")의 경우 매기변수(parameter)의 형태에 대한 주석이다.
[python 문법] self와 __init__ :
class 사용 X :
def function_x(AAA):
print(AAA)
class 사용 O :
class Class_Y:
def __init__(self, AAA):
self.AAA = AAA
def function_x(self):
print(self.AAA)클래스 구성을 사용하면 글로벌 변수 없애고, 모든 변수를 어떤 스코프에 소속시킬 수 있다. 또한 함수 실행 도중, 함수 자신을 다시 호출하는 처리 등이 가능하게 한다.
[인스턴스]
여기서 클래스에 정의된 데이터나 함수를 사용하기 위해 인스턴스(클래스를 실체화한 것)를 생성해야 한다.
B = Class_Y("value_Z")위의 코드에서 'B'가 바로 인스턴스이다. Class_Y의 인스턴스가 B에 할당되어 있다.
지금까지의 코드를 하나의 코드블록으로 작성하면, 다음과 같다.
class Class_Y:
def __init__(self,AAA):
self.AAA = AAA
def function_X(self):
print(self.AAA)
B = Class_Y("value_Z")
B.function_X()함수에서 print 내장함수를 사용하고 있으므로 value_Z가 리턴된다.
[메소드]
클래스 내에 기재되어 있는 함수를 메소드라고 한다.
class Class_Y:
def __init__(self,AAA):
self.AAA = AAA
def function_X_1(self): #메소드1
print(self.AAA)
def function_X_2(self): #메소드2
return self.AAA
[self]
그 시점의 자신, 인스턴스 자신
[__init__]
컨스트럭터. 초기화를 위한 매소드(함수)이다. 인스턴스화를 실시할 때 반드시 처음에 호출되는 함수이며 인스턴스 생성과 관련하여 데이터의 초기화를 실시하는 함수이다.
+ 객체지향에 관한 추가 설명 )
class는 붕어빵 틀, object는 붕어빵으로 생각하면 쉽다.
Person이라는 class(붕어빵 틀)이 있다고 하자. Person(class)에 'age', 'name', 'gender'라는 변수를 생성할 수 있고, 'speak()', 'walk()' 라는 함수를 추가할 수 있다.
이제, 붕어빵 틀을 이용하여 쉽게 붕어빵(object)을 만드려고 한다. Person에 해당하는 Yujin이라는 Object를 만드려고 한다.
Yujin.age = 24 (전역적으로 이용할 때)
혹은
class Yujin:
self.age = 24 (해당 클래스 내에서)
위와 같이 정의할 수 있다.
torch.Tensor
torch>torch.tensor
: a multi-dimensional matrix containing elements of a single data type

데이터를 저장하는 다차원 행렬이라고 생각하면 된다. 맨 위의 코드에서 입력값과 반환값의 형식은 다차원 행렬임을 나타내기 위해 사용되었다.
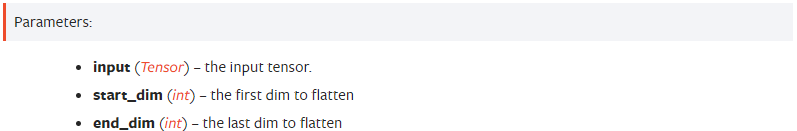
torch.flatten
torch>torch.flatten

다차원 배열 입력을 1차원 배열로 변환하는 역할을 한다. reshape이 이루어지더라도 input 배열의 순서는 변하지 않는다.
https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/main/torchvision/models/alexnet.py
GitHub - pytorch/vision: Datasets, Transforms and Models specific to Computer Vision
Datasets, Transforms and Models specific to Computer Vision - GitHub - pytorch/vision: Datasets, Transforms and Models specific to Computer Vision
github.com
from functools import partial
from typing import Any, Optional
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from ..transforms._presets import ImageClassification
from ..utils import _log_api_usage_once
from ._api import register_model, Weights, WeightsEnum
from ._meta import _IMAGENET_CATEGORIES
from ._utils import _ovewrite_named_param, handle_legacy_interface
__all__ = ["AlexNet", "AlexNet_Weights", "alexnet"]
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes: int = 1000, dropout: float = 0.5) -> None:
super().__init__()
_log_api_usage_once(self)
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((6, 6))
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=dropout),
nn.Linear(256 * 6 * 6, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=dropout),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),
)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x = self.features(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
class AlexNet_Weights(WeightsEnum):
IMAGENET1K_V1 = Weights(
url="https://download.pytorch.org/models/alexnet-owt-7be5be79.pth",
transforms=partial(ImageClassification, crop_size=224),
meta={
"num_params": 61100840,
"min_size": (63, 63),
"categories": _IMAGENET_CATEGORIES,
"recipe": "https://github.com/pytorch/vision/tree/main/references/classification#alexnet-and-vgg",
"_metrics": {
"ImageNet-1K": {
"acc@1": 56.522,
"acc@5": 79.066,
}
},
"_ops": 0.714,
"_weight_size": 233.087,
"_docs": """
These weights reproduce closely the results of the paper using a simplified training recipe.
""",
},
)
DEFAULT = IMAGENET1K_V1
@register_model()
@handle_legacy_interface(weights=("pretrained", AlexNet_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V1))
def alexnet(*, weights: Optional[AlexNet_Weights] = None, progress: bool = True, **kwargs: Any) -> AlexNet:
"""AlexNet model architecture from `One weird trick for parallelizing convolutional neural networks <https://arxiv.org/abs/1404.5997>`__.
.. note::
AlexNet was originally introduced in the `ImageNet Classification with
Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
<https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2012/hash/c399862d3b9d6b76c8436e924a68c45b-Abstract.html>`__
paper. Our implementation is based instead on the "One weird trick"
paper above.
Args:
weights (:class:`~torchvision.models.AlexNet_Weights`, optional): The
pretrained weights to use. See
:class:`~torchvision.models.AlexNet_Weights` below for
more details, and possible values. By default, no pre-trained
weights are used.
progress (bool, optional): If True, displays a progress bar of the
download to stderr. Default is True.
**kwargs: parameters passed to the ``torchvision.models.squeezenet.AlexNet``
base class. Please refer to the `source code
<https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/main/torchvision/models/alexnet.py>`_
for more details about this class.
.. autoclass:: torchvision.models.AlexNet_Weights
:members:
"""
weights = AlexNet_Weights.verify(weights)
if weights is not None:
_ovewrite_named_param(kwargs, "num_classes", len(weights.meta["categories"]))
model = AlexNet(**kwargs)
if weights is not None:
model.load_state_dict(weights.get_state_dict(progress=progress))
return model
# The dictionary below is internal implementation detail and will be removed in v0.15
from ._utils import _ModelURLs
model_urls = _ModelURLs(
{
"alexnet": AlexNet_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V1.url,
}
)'AI&ML > 논문리뷰' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [논문리뷰] You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection (YOLOv1) (0) | 2023.02.22 |
|---|---|
| AlexNet 구현 코드 분석 1 (0) | 2023.01.05 |

